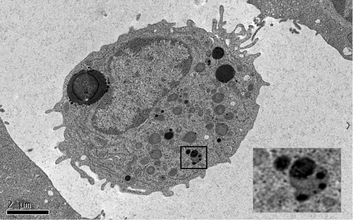
 Blood monocyte 48 hrs after infusion of USPIO. Magnified inset
Blood monocyte 48 hrs after infusion of USPIO. Magnified inset shows USPIO within lysosome. (From Alam et al under CC-BY)
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
Guidelines for Safe Administration of Ferumoxytol Contrast
Use of ferumoxytol is currently limited to patients with known contraindications to gadolinium contrast agents, such as severe renal insufficiency or allergic reactions. Of course, it should not be given to patients allergic to IV iron products or iron overload states.
The most common reactions, occurring in less than 2% in aggregate, include hypertension, nausea, flushing, backache, pruritus, headache, and vomiting. There is no evidence that ferumoxytol causes renal injury as primary excretion is through the liver and bowel.
Feraheme, the commercial version of ferumoxytol in the USA, is marketed as a single-dose 17-mm vial containing 510 mg of iron and costs approximately $700. Generally no more than a half-bottle is used for imaging. The typical dose is 3 mg ferumoxytol/kg of body weight, with a range of 1-5 allowed. It should be diluted in a 1:4 ratio with normal saline and injected by slow IV infusion over 15 minutes. Vital signs should be measured before, 5 and 30 minutes after administration of ferumoxytol. It is advised that patients be observed an additional 30 minutes in the MRI center after their exam is completed. The need for a slow infusion is highlighted by the FDA “black box warning” issued in 2015, resulting from several deaths and severe reactions to the rapid administration of the drug as a therapeutic agent. See package insert in References for more details.
ACR Committee on Drugs and Contrast Agents. ACR Manual on Contrast Agents, 2024. American College of Radiology, 2024.
Aghighi M, Golovko D, Ansari C, et al. Imaging tumor necrosis with ferumoxytol. PLOS ONE 2015; 10(11):e0142665
Ahmad F, Treanor L, McGrath TA, et al. Safety of off-label use of ferumoxytol as a contrast agent for MRI: A systematic review and meta-analysis of adverse events. J Magn Reson Imaging 2021; 53:840-858. [DOI LINK]
Alam SR, Stirrat C, Richards J, et al. Vascular and plaque imaging with ultrasmall super paramagnetic particles of iron oxide. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2015; 17:83.
Bashir MR, Bhatti L, Marin D, Nelson RC. Emerging applications for ferumoxytol as a contrast agent in MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 2015; 41:884-898.
Daldrup-Link HE. Ten things you might not know about iron oxide nanoparticles. Radiology 2017; 284:616-629.
Feraheme™ package insert, from www.feraheme.com (assessed 6/19/20)
Nguyen K-L, Park E-A, Yoshida T, et al. Ferumoxytol-enhanced black-blood cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2017; 19:106.
Nguyen K-L, Yoshida T, Kathuria-Prakash N, et al. Multicenter safety and practice for off-label diagnostic use of ferumoxytol in MRI. Radiology 2019; 293:554-564.
Schieda N. Parenteral ferumoxytol interaction with magnetic resonance imaging: a case report, review of the literature and advisory warning. Insights Imaging 2013; 4:509-512.
Storey P, Lim RP, Chandarana H, et al. MRI assessment of hepatic iron clearance rates as USPIO administration in healthy adults. Invest Radiol 2012; 47:717-724.
Toth GB, Varallyay CG, Horvath A, et al. Current and potential imaging applications of ferumoxytol for magnetic resonance imaging. Kidney Int 2017; 92:47-66.
What is meant by the relaxivity of a contrast agent? How is it measured?
I have heard there are MR contrast agents for lymph nodes. How do these work?